ω 2 f 2 (ωk + ifl) and ˆ v = ω 2 2 u ʹ = Re[ u ˆ e i(kx+ly ωt ) ], v ʹ = Re[ˆ v e i(kx +ly ωt ) ], and h ʹ = Re[ h ˆ e i(kx+ly ωt ) ].
|
|
|
- Erik Pope
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 28) Show that for the gravity wave modes supported in the shallow water system linearized about a basic state at rest, the complex amplitudes of the zonal and meridional winds are given by: u = g h ω 2 2 (ωk + ifl) and v = ω 2 2 (ωl ifk), respectively First, start with the linearized equations: u t v = g h x, v t + f u = g h y, h t + H( u x + v y ) = 0, where u = Re[ u e i(kx+ly ωt ) ], v = Re[ v e i(kx +ly ωt ) ], and h = Re[ h e i(kx+ly ωt ) ] After taking the derivatives, the linearized equations can be written as listed below u iωe i(kx +ly ωt ) v e i(kx +ly ωt ) = i(kx +ly ωt ) ike v iωe i(kx +ly ωt ) + f u e i(kx +ly ωt ) = i(kx +ly ωt ) ile h iωe i(kx +ly ωt ) + He i(kx+ly ωt ) ( u ik + v il) = 0 Simplifying these equations we get: A u iω v = ik B v iω + f u = il C h iω + H( u ik + v il) = 0 In order to find u let s take iωa B, which yields u i 2 ω 2 iωfv + iωfv 2 u = i 2 kω + fil => u (ω 2 2 ) = (ωk + ifl) => u = (ωk + ifl) (ω 2 2 ) To find v, we can take fa + iωb, which yields u fiω 2 v + i 2 ω 2 v + iωf u = fik ωi 2 l => v (ω 2 2 ) = (ωl ifk) => v = (ωl ifk) (ω 2 2 )
3 29) Using u = u = v = g h ω 2 2 (ωk + ifl) and v = ω 2 2 (ωl ifk), show that ω 2 2 [ωk cos(kx + ly ωt) lsin(kx + ly ωt)], and ω 2 2 [ωlcos(kx + ly ωt) + kf sin(kx + ly ωt)] Solve for u : u = Re[ u e i(kx+ly ωt ) ] = Re[ u (cos(kx + ly ωt) + isin(kx + ly ωt))] Substitute u into the equation to get: u = Re[ w 2 2 ((ωk + ifl)(cos(kx + ly ωt) + isin(kx + ly ωt)))] Expand to get Re[ w 2 (ωk cos(kx + ly ωt) + iωk sin(kx + ly ωt) + iflcos(kx + ly ωt) + 2 i2 flsin(kx + ly ωt))] Taking the real part of the above expression yields: u = w 2 (ωk cos(kx + ly ωt) lsin(kx + ly ωt)) 2 Solve for v : v = Re[ v e i(kx +ly ωt ) ] = Re[ v (cos(kx + ly ωt) + isin(kx + ly ωt))] Substitute v into the equation and expand to get: Re[ w 2 (ωlcos(kx + ly ωt) + iωlsin(kx + ly ωt) ifk cos(kx + ly ωt) 2 i2 fk sin(kx + ly ωt))] Finally, taking the real part yields: v = w 2 (ωlcos(kx + ly ωt) + fk sin(kx + ly ωt)) 2
4 31) Linearize the 2D, non- divergent, barotropic, vorticity equation on a β - plane and find the dispersion relationship for ψ = Uy and ψ = Re[ ψ e i(kx +ly wt ) ] First, linearize the vorticity equation: ζ ζ = u t x v ζ y βv Set ζ = ζ + ζ, u = u + u, and v = v + v Set the basic state as ζ t The linearized equation becomes: ζ = u x v ζ βv = 0 y t (ζ + ζ ) = (u + u ) x (ζ + ζ ) (v + v ) y (ζ + ζ ) β(v + v ) Expanding this, we now have: ζ t + ζ = (u ζ t x + u ζ x + u ζ x + u ζ ζ ) (v x y + v ζ y + v ζ y + v ζ ) βv β y v Now let s simplify Start by removing the basic state since it has been set to zero ζ t = (u ζ x + u ζ x + u ζ x ) (v ζ y + v ζ y + v ζ y ) βv Now get rid of the non- linear terms to get the final equation ζ t = u ζ x u ζ x v ζ y v ζ y βv In order to find the dispersion relationship, let us re- write this equation in terms of ψ Recall: ζ = 2 ψ, u = ψ ψ, and v = Substituting these in we get, y x t ( 2 ψ ) = ψ y x ( 2 ψ ) + ψ y x ( 2 ψ ) ψ x y ( 2 ψ ) ψ x y ( 2 ψ ) β ψ x However, we know that ψ = Uy, so ψ x = 2 ψ = 0 and ψ = U, giving us: y t ( 2 ψ ) = U x ( 2 ψ ) β ψ x
5 Now use ψ = Re[ ψ e i(kx +ly wt ) ] and take the appropriate derivatives to get: iω(i 2 k 2 + i 2 l 2 ) ψ e i(kx +ly ωt ) = Uik(i 2 k 2 + i 2 l 2 ) ψ e i(kx +ly ωt ) βik ψ e i(kx+ly ωt ) This simplifies to ω(k 2 + l 2 ) = Uk(k 2 + l 2 ) βk To get the dispersion relationship, solve for ω ω = Uk(k 2 + l 2 ) βk (k 2 + l 2 ), which can finally be simplified to ω = Uk βk (k 2 + l 2 ) The phase speed of these waves, c = ω k = U therefore, these waves are dispersive β, depends on the wave number; (k 2 + l 2 ) 32) (Holton 71) Show that F(x) = Re[Cexp(imx)] can also be written as F(x) = C cos(m(x x o )), where x o = m 1 sin 1 ( C i C ) First, we know that F(x) = Re[Cexp(imx)] can be expanded to F(x) = Re[Ccos(mx) + ic sin(mx)], where C = C r + ic i => F(x) = Re[C r cos(mx) + ic i cos(mx) + ic r sin(mx) C i sin(mx)] Taking the real part of the equation we get, F(x) = C r cos(mx) C i sin(mx) Now we need to find C r and C i From x o = m 1 sin 1 ( C i C ) we get C i = C sin(mx o ) Define C r = C cos(mx o ) and plug them into F(x) The resulting equation is: F(x) = Re[C cos(mx)cos(mx o ) C sin(mx)sin(mx o )]
6 Using the trig identity, cos(a)cos(b) sin(a)sin(b) = cos(a b), we get the final equation: F(x) = C cos(m(x x o )) 33) (Holton 72) Show that ψ = Acos(kx vt kx o )exp(αt) can be written as ψ = Re[Be ik(x ct ) ] Find B i,b r,c i,c r in terms of A, α, v, and x o By defining C = c r + ic i we can re- write ψ as, ψ = Re[Be ik(x c r t ) ]e kc i t Using the rule from problem 71 we can further write, ψ = Re[Be ik(x c r t ) ]e kc i t = Re[ B cos(k(x c r t) kx o )]e kc i t Now, let v = kc r, and α = kc i => ψ = Re[ B cos(kx vt kx o )]exp(αt) Similarly to 71, define x o = k 1 sin 1 ( B i B ) Giving us B r = Acos(kx o ) and B i = Asin(kx o ) Now we have, ψ = Acos(kx vt kx o )exp(αt)
7
8
) 2 ψ +β ψ. x = 0. (71) ν = uk βk/k 2, (74) c x u = β/k 2. (75)
 3 Rossby Waves 3.1 Free Barotropic Rossby Waves The dispersion relation for free barotropic Rossby waves can be derived by linearizing the barotropic vortiticy equation in the form (21). This equation
3 Rossby Waves 3.1 Free Barotropic Rossby Waves The dispersion relation for free barotropic Rossby waves can be derived by linearizing the barotropic vortiticy equation in the form (21). This equation
Waves Primer II Basic wave form. Waves are: 1. Important 2. Easy 3. Neat
 Waves Primer II Waves are: 1. Important 2. Easy 3. Neat 23.1 Basic wave form The wave form that you will almost always use is a = Re[A c e i(kx+ly ωt) ] (23.1) Where a variable A c waveamplitude(complexinthiscase)
Waves Primer II Waves are: 1. Important 2. Easy 3. Neat 23.1 Basic wave form The wave form that you will almost always use is a = Re[A c e i(kx+ly ωt) ] (23.1) Where a variable A c waveamplitude(complexinthiscase)
6 Two-layer shallow water theory.
 6 Two-layer shallow water theory. Wewillnowgoontolookatashallowwatersystemthathastwolayersofdifferent density. This is the next level of complexity and a simple starting point for understanding the behaviour
6 Two-layer shallow water theory. Wewillnowgoontolookatashallowwatersystemthathastwolayersofdifferent density. This is the next level of complexity and a simple starting point for understanding the behaviour
9 Rossby Waves. 9.1 Non-divergent barotropic vorticity equation. CSU ATS601 Fall (Holton Chapter 7, Vallis Chapter 5)
 9 Rossby Waves (Holton Chapter 7, Vallis Chapter 5) 9.1 Non-divergent barotropic vorticity equation We are now at a point that we can discuss our first fundamental application of the equations of motion:
9 Rossby Waves (Holton Chapter 7, Vallis Chapter 5) 9.1 Non-divergent barotropic vorticity equation We are now at a point that we can discuss our first fundamental application of the equations of motion:
Chapter 9. Barotropic Instability. 9.1 Linearized governing equations
 Chapter 9 Barotropic Instability The ossby wave is the building block of low ossby number geophysical fluid dynamics. In this chapter we learn how ossby waves can interact with each other to produce a
Chapter 9 Barotropic Instability The ossby wave is the building block of low ossby number geophysical fluid dynamics. In this chapter we learn how ossby waves can interact with each other to produce a
The dynamics of a simple troposphere-stratosphere model
 The dynamics of a simple troposphere-stratosphere model by Jessica Duin under supervision of Prof. Dr. A. Doelman, UvA Dr. W.T.M. Verkley, KNMI August 31, 25 Universiteit van Amsterdam Korteweg-de vries
The dynamics of a simple troposphere-stratosphere model by Jessica Duin under supervision of Prof. Dr. A. Doelman, UvA Dr. W.T.M. Verkley, KNMI August 31, 25 Universiteit van Amsterdam Korteweg-de vries
= g h fu (22.2) Dh u. x + v ) fv = fu = 0 (22.4) = g h. x + v v. + h
 Lecture 22 22.1 Barotropic waves, no rotation We ll spend the class talking about various barotropic waves. Baroclinic waves are very, very, important, but I ll be leaving them to others. Since we ve already
Lecture 22 22.1 Barotropic waves, no rotation We ll spend the class talking about various barotropic waves. Baroclinic waves are very, very, important, but I ll be leaving them to others. Since we ve already
Chapter 13 Instability on non-parallel flow Introduction and formulation
 Chapter 13 Instability on non-parallel flow. 13.1 Introduction and formulation We have concentrated our discussion on the instabilities of parallel, zonal flows. There is the largest amount of literature
Chapter 13 Instability on non-parallel flow. 13.1 Introduction and formulation We have concentrated our discussion on the instabilities of parallel, zonal flows. There is the largest amount of literature
AFRICAN EASTERLY WAVES IN CURRENT AND FUTURE CLIMATES
 AFRICAN EASTERLY WAVES IN CURRENT AND FUTURE CLIMATES Victoria Dollar RTG Seminar Research - Spring 2018 April 16, 2018 Victoria Dollar ASU April 16, 2018 1 / 26 Overview Introduction Rossby waves and
AFRICAN EASTERLY WAVES IN CURRENT AND FUTURE CLIMATES Victoria Dollar RTG Seminar Research - Spring 2018 April 16, 2018 Victoria Dollar ASU April 16, 2018 1 / 26 Overview Introduction Rossby waves and
Figure 1: Surface waves
 4 Surface Waves on Liquids 1 4 Surface Waves on Liquids 4.1 Introduction We consider waves on the surface of liquids, e.g. waves on the sea or a lake or a river. These can be generated by the wind, by
4 Surface Waves on Liquids 1 4 Surface Waves on Liquids 4.1 Introduction We consider waves on the surface of liquids, e.g. waves on the sea or a lake or a river. These can be generated by the wind, by
PHYS 408, Optics. Problem Set 1 - Spring Posted: Fri, January 8, 2015 Due: Thu, January 21, 2015.
 PHYS 408, Optics Problem Set 1 - Spring 2016 Posted: Fri, January 8, 2015 Due: Thu, January 21, 2015. 1. An electric field in vacuum has the wave equation, Let us consider the solution, 2 E 1 c 2 2 E =
PHYS 408, Optics Problem Set 1 - Spring 2016 Posted: Fri, January 8, 2015 Due: Thu, January 21, 2015. 1. An electric field in vacuum has the wave equation, Let us consider the solution, 2 E 1 c 2 2 E =
Concepts from linear theory Extra Lecture
 Concepts from linear theory Extra Lecture Ship waves from WW II battleships and a toy boat. Kelvin s (1887) method of stationary phase predicts both. Concepts from linear theory A. Linearize the nonlinear
Concepts from linear theory Extra Lecture Ship waves from WW II battleships and a toy boat. Kelvin s (1887) method of stationary phase predicts both. Concepts from linear theory A. Linearize the nonlinear
Traveling Harmonic Waves
 Traveling Harmonic Waves 6 January 2016 PHYC 1290 Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Functional Form for Traveling Waves We can show that traveling waves whose shape does not change with time
Traveling Harmonic Waves 6 January 2016 PHYC 1290 Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Functional Form for Traveling Waves We can show that traveling waves whose shape does not change with time
WAVE PACKETS & SUPERPOSITION
 1 WAVE PACKETS & SUPERPOSITION Reading: Main 9. PH41 Fourier notes 1 x k Non dispersive wave equation x ψ (x,t) = 1 v t ψ (x,t) So far, we know that this equation results from application of Newton s law
1 WAVE PACKETS & SUPERPOSITION Reading: Main 9. PH41 Fourier notes 1 x k Non dispersive wave equation x ψ (x,t) = 1 v t ψ (x,t) So far, we know that this equation results from application of Newton s law
Periodic functions: simple harmonic oscillator
 Periodic functions: simple harmonic oscillator Recall the simple harmonic oscillator (e.g. mass-spring system) d 2 y dt 2 + ω2 0y = 0 Solution can be written in various ways: y(t) = Ae iω 0t y(t) = A cos
Periodic functions: simple harmonic oscillator Recall the simple harmonic oscillator (e.g. mass-spring system) d 2 y dt 2 + ω2 0y = 0 Solution can be written in various ways: y(t) = Ae iω 0t y(t) = A cos
10 Shallow Water Models
 10 Shallow Water Models So far, we have studied the effects due to rotation and stratification in isolation. We then looked at the effects of rotation in a barotropic model, but what about if we add stratification
10 Shallow Water Models So far, we have studied the effects due to rotation and stratification in isolation. We then looked at the effects of rotation in a barotropic model, but what about if we add stratification
MET 4302 Midterm Study Guide 19FEB18
 The exam will be 4% short answer and the remainder (6%) longer (1- aragrahs) answer roblems and mathematical derivations. The second section will consists of 6 questions worth 15 oints each. Answer 4.
The exam will be 4% short answer and the remainder (6%) longer (1- aragrahs) answer roblems and mathematical derivations. The second section will consists of 6 questions worth 15 oints each. Answer 4.
Math 489AB A Very Brief Intro to Fourier Series Fall 2008
 Math 489AB A Very Brief Intro to Fourier Series Fall 8 Contents Fourier Series. The coefficients........................................ Convergence......................................... 4.3 Convergence
Math 489AB A Very Brief Intro to Fourier Series Fall 8 Contents Fourier Series. The coefficients........................................ Convergence......................................... 4.3 Convergence
= k, (2) p = h λ. x o = f1/2 o a. +vt (4)
 Traveling Functions, Traveling Waves, and the Uncertainty Principle R.M. Suter Department of Physics, Carnegie Mellon University Experimental observations have indicated that all quanta have a wave-like
Traveling Functions, Traveling Waves, and the Uncertainty Principle R.M. Suter Department of Physics, Carnegie Mellon University Experimental observations have indicated that all quanta have a wave-like
Chapter 4: Ocean waves
 Chapter 4: Ocean waves 4.1 Wave concepts When we think about waves usually we have a picture of undulations on the surface of the sea or lakes. They usually progress from a region of formation to a coast
Chapter 4: Ocean waves 4.1 Wave concepts When we think about waves usually we have a picture of undulations on the surface of the sea or lakes. They usually progress from a region of formation to a coast
A Uniform PV Framework for Balanced Dynamics
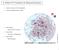 A Uniform PV Framework for Balanced Dynamics vertical structure of the troposphere surface quasigeostrophic models Dave Muraki Simon Fraser University Greg Hakim University of Washington Chris Snyder NCAR
A Uniform PV Framework for Balanced Dynamics vertical structure of the troposphere surface quasigeostrophic models Dave Muraki Simon Fraser University Greg Hakim University of Washington Chris Snyder NCAR
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c. Lecture 11 Dispersion
 Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 11 Dispersion What We Did Last Time Defined Fourier transform f (t) = F(ω)e iωt dω F(ω) = 1 2π f(t) and F(w) represent a function in time and frequency domains Analyzed
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 11 Dispersion What We Did Last Time Defined Fourier transform f (t) = F(ω)e iωt dω F(ω) = 1 2π f(t) and F(w) represent a function in time and frequency domains Analyzed
THE PHYSICS OF WAVES CHAPTER 1. Problem 1.1 Show that Ψ(x, t) = (x vt) 2. is a traveling wave.
 CHAPTER 1 THE PHYSICS OF WAVES Problem 1.1 Show that Ψ(x, t) = (x vt) is a traveling wave. Show thatψ(x, t) is a wave by substitutioninto Equation 1.1. Proceed as in Example 1.1. On line version uses Ψ(x,
CHAPTER 1 THE PHYSICS OF WAVES Problem 1.1 Show that Ψ(x, t) = (x vt) is a traveling wave. Show thatψ(x, t) is a wave by substitutioninto Equation 1.1. Proceed as in Example 1.1. On line version uses Ψ(x,
Wave mo(on in the tropics. Shayne McGregor Lecturer (Climate), EAE, Monash Associate Inves(gator (ARC CSS)
 Wave mo(on in the tropics Shayne McGregor Lecturer (Climate), EAE, Monash Associate Inves(gator (ARC CSS) Equatorially trapped waves The linear SWM Equatorial Kelvin waves Other equatorially trapped waves
Wave mo(on in the tropics Shayne McGregor Lecturer (Climate), EAE, Monash Associate Inves(gator (ARC CSS) Equatorially trapped waves The linear SWM Equatorial Kelvin waves Other equatorially trapped waves
Symmetry methods in dynamic meteorology
 Symmetry methods in dynamic meteorology p. 1/12 Symmetry methods in dynamic meteorology Applications of Computer Algebra 2008 Alexander Bihlo alexander.bihlo@univie.ac.at Department of Meteorology and
Symmetry methods in dynamic meteorology p. 1/12 Symmetry methods in dynamic meteorology Applications of Computer Algebra 2008 Alexander Bihlo alexander.bihlo@univie.ac.at Department of Meteorology and
13.42 LECTURE 2: REVIEW OF LINEAR WAVES
 13.42 LECTURE 2: REVIEW OF LINEAR WAVES SPRING 2003 c A.H. TECHET & M.S. TRIANTAFYLLOU 1. Basic Water Waves Laplace Equation 2 φ = 0 Free surface elevation: z = η(x, t) No vertical velocity at the bottom
13.42 LECTURE 2: REVIEW OF LINEAR WAVES SPRING 2003 c A.H. TECHET & M.S. TRIANTAFYLLOU 1. Basic Water Waves Laplace Equation 2 φ = 0 Free surface elevation: z = η(x, t) No vertical velocity at the bottom
Superposition of electromagnetic waves
 Superposition of electromagnetic waves February 9, So far we have looked at properties of monochromatic plane waves. A more complete picture is found by looking at superpositions of many frequencies. Many
Superposition of electromagnetic waves February 9, So far we have looked at properties of monochromatic plane waves. A more complete picture is found by looking at superpositions of many frequencies. Many
Lecture 4. 1 de Broglie wavelength and Galilean transformations 1. 2 Phase and Group Velocities 4. 3 Choosing the wavefunction for a free particle 6
 Lecture 4 B. Zwiebach February 18, 2016 Contents 1 de Broglie wavelength and Galilean transformations 1 2 Phase and Group Velocities 4 3 Choosing the wavefunction for a free particle 6 1 de Broglie wavelength
Lecture 4 B. Zwiebach February 18, 2016 Contents 1 de Broglie wavelength and Galilean transformations 1 2 Phase and Group Velocities 4 3 Choosing the wavefunction for a free particle 6 1 de Broglie wavelength
EECS 20N: Midterm 2 Solutions
 EECS 0N: Midterm Solutions (a) The LTI system is not causal because its impulse response isn t zero for all time less than zero. See Figure. Figure : The system s impulse response in (a). (b) Recall that
EECS 0N: Midterm Solutions (a) The LTI system is not causal because its impulse response isn t zero for all time less than zero. See Figure. Figure : The system s impulse response in (a). (b) Recall that
Physics 218 Quantum Mechanics I Assignment 6
 Physics 218 Quantum Mechanics I Assignment 6 Logan A. Morrison February 17, 2016 Problem 1 A non-relativistic beam of particles each with mass, m, and energy, E, which you can treat as a plane wave, is
Physics 218 Quantum Mechanics I Assignment 6 Logan A. Morrison February 17, 2016 Problem 1 A non-relativistic beam of particles each with mass, m, and energy, E, which you can treat as a plane wave, is
Traveling Waves: Energy Transport
 Traveling Waves: Energ Transport wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energ but not matter. Intensit: I P power rea Intensit I power per unit area (measured in Watts/m 2 ) Intensit is proportional
Traveling Waves: Energ Transport wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energ but not matter. Intensit: I P power rea Intensit I power per unit area (measured in Watts/m 2 ) Intensit is proportional
Atmospheric Dynamics: lecture 11
 Atmospheric Dynamics: lecture 11 (http://www.staff.science.uu.nl/~delde102/) Chapter 9 Baroclinic waves and cyclogenesis What is a baroclinic wave? Quasi-geostrophic equations Omega equation Original articles:
Atmospheric Dynamics: lecture 11 (http://www.staff.science.uu.nl/~delde102/) Chapter 9 Baroclinic waves and cyclogenesis What is a baroclinic wave? Quasi-geostrophic equations Omega equation Original articles:
Dispersive nonlinear partial differential equations
 Dispersive nonlinear partial differential equations Elena Kartashova 16.02.2007 Elena Kartashova (RISC) Dispersive nonlinear PDEs 16.02.2007 1 / 25 Mathematical Classification of PDEs based on the FORM
Dispersive nonlinear partial differential equations Elena Kartashova 16.02.2007 Elena Kartashova (RISC) Dispersive nonlinear PDEs 16.02.2007 1 / 25 Mathematical Classification of PDEs based on the FORM
Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics
 1896 190 1987 006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA35) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University
1896 190 1987 006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA35) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University
1/27/2010. With this method, all filed variables are separated into. from the basic state: Assumptions 1: : the basic state variables must
 Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method With this method, all filed variables are separated into two parts: (a) a basic state part and (b) a deviation from the basic state: Perturbation Method
Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method With this method, all filed variables are separated into two parts: (a) a basic state part and (b) a deviation from the basic state: Perturbation Method
Lecture 4: Oscillators to Waves
 Matthew Schwartz Lecture 4: Oscillators to Waves Review two masses Last time we studied how two coupled masses on springs move If we take κ=k for simplicity, the two normal modes correspond to ( ) ( )
Matthew Schwartz Lecture 4: Oscillators to Waves Review two masses Last time we studied how two coupled masses on springs move If we take κ=k for simplicity, the two normal modes correspond to ( ) ( )
Waves Solutions to the Wave Equation Sine Waves Transverse Speed and Acceleration
 Waves Solutions to the Wave Equation Sine Waves Transverse Speed and Acceleration Lana Sheridan De Anza College May 17, 2018 Last time pulse propagation the wave equation Overview solutions to the wave
Waves Solutions to the Wave Equation Sine Waves Transverse Speed and Acceleration Lana Sheridan De Anza College May 17, 2018 Last time pulse propagation the wave equation Overview solutions to the wave
ESCI 343 Atmospheric Dynamics II Lesson 11 - Rossby Waves
 ESCI 343 Atmospheric Dynamics II Lesson 11 - Rossby Waves Reference: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (4 rd edition), J.R. Holton Atmosphere-Ocean Dynamics, A.E. Gill Fundamentals of Atmospheric
ESCI 343 Atmospheric Dynamics II Lesson 11 - Rossby Waves Reference: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (4 rd edition), J.R. Holton Atmosphere-Ocean Dynamics, A.E. Gill Fundamentals of Atmospheric
Waves, the Wave Equation, and Phase Velocity. We ll start with optics. The one-dimensional wave equation. What is a wave? Optional optics texts: f(x)
 We ll start with optics Optional optics texts: Waves, the Wave Equation, and Phase Velocity What is a wave? f(x) f(x-) f(x-) f(x-3) Eugene Hecht, Optics, 4th ed. J.F. James, A Student's Guide to Fourier
We ll start with optics Optional optics texts: Waves, the Wave Equation, and Phase Velocity What is a wave? f(x) f(x-) f(x-) f(x-3) Eugene Hecht, Optics, 4th ed. J.F. James, A Student's Guide to Fourier
Physics 443, Solutions to PS 1 1
 Physics 443, Solutions to PS. Griffiths.9 For Φ(x, t A exp[ a( mx + it], we need that + h Φ(x, t dx. Using the known result of a Gaussian intergral + exp[ ax ]dx /a, we find that: am A h. ( The Schrödinger
Physics 443, Solutions to PS. Griffiths.9 For Φ(x, t A exp[ a( mx + it], we need that + h Φ(x, t dx. Using the known result of a Gaussian intergral + exp[ ax ]dx /a, we find that: am A h. ( The Schrödinger
Wave interactions. J. Vanneste. School of Mathematics University of Edinburgh, UK. vanneste < > - + Wave interactions p.
 Wave interactions J. Vanneste School of Mathematics University of Edinburgh, UK www.maths.ed.ac.uk/ vanneste Wave interactions p.1/50 Linear waves in conservative systems Small amplitude motion: linearize
Wave interactions J. Vanneste School of Mathematics University of Edinburgh, UK www.maths.ed.ac.uk/ vanneste Wave interactions p.1/50 Linear waves in conservative systems Small amplitude motion: linearize
The Schroedinger equation
 The Schroedinger equation After Planck, Einstein, Bohr, de Broglie, and many others (but before Born), the time was ripe for a complete theory that could be applied to any problem involving nano-scale
The Schroedinger equation After Planck, Einstein, Bohr, de Broglie, and many others (but before Born), the time was ripe for a complete theory that could be applied to any problem involving nano-scale
1 (2n)! (-1)n (θ) 2n
 Complex Numbers and Algebra The real numbers are complete for the operations addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, or more suggestively, for the operations of addition and multiplication
Complex Numbers and Algebra The real numbers are complete for the operations addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, or more suggestively, for the operations of addition and multiplication
( ) (9.1.1) Chapter 9. Geostrophy, Quasi-Geostrophy and the Potential Vorticity Equation. 9.1 Geostrophy and scaling.
 Chapter 9 Geostrophy, Quasi-Geostrophy and the Potential Vorticity Equation 9.1 Geostrophy and scaling. We examined in the last chapter some consequences of the dynamical balances for low frequency, nearly
Chapter 9 Geostrophy, Quasi-Geostrophy and the Potential Vorticity Equation 9.1 Geostrophy and scaling. We examined in the last chapter some consequences of the dynamical balances for low frequency, nearly
Chapter 2 Solutions. Chapter 2 Solutions 1. 4( z t) ( z t) z t
 Chapter Solutions 1 Chapter Solutions.1. 1 z t ( z t) z z ( z t) t t It s a twice differentiable function of ( z t ), where is in the negative z direction. 1 y t ( y, t) ( y4 t) ( y 4 t) y y 8( y 4 t)
Chapter Solutions 1 Chapter Solutions.1. 1 z t ( z t) z z ( z t) t t It s a twice differentiable function of ( z t ), where is in the negative z direction. 1 y t ( y, t) ( y4 t) ( y 4 t) y y 8( y 4 t)
Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modelling
 M.Sc. in Computational Science Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modelling Peter Lynch, Met Éireann Mathematical Computation Laboratory (Opp. Room 30) Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. January April, 2004.
M.Sc. in Computational Science Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modelling Peter Lynch, Met Éireann Mathematical Computation Laboratory (Opp. Room 30) Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. January April, 2004.
Dispersion (3A) 1-D Dispersion. Young W. Lim 10/15/13
 1-D Dispersion Copyright (c) 013. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1. or any later version published
1-D Dispersion Copyright (c) 013. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1. or any later version published
observational data analysis (Supplementary Material)
 1 Assessing the equatorial long-wave approximation: asymptotics and observational data analysis (Supplementary Material) 3 by H. Reed Ogrosky and Samuel N. Stechmann 4 1. Kelvin and MRG waves 5 6 The analysis
1 Assessing the equatorial long-wave approximation: asymptotics and observational data analysis (Supplementary Material) 3 by H. Reed Ogrosky and Samuel N. Stechmann 4 1. Kelvin and MRG waves 5 6 The analysis
Time Series Analysis. Solutions to problems in Chapter 7 IMM
 Time Series Analysis Solutions to problems in Chapter 7 I Solution 7.1 Question 1. As we get by subtraction kx t = 1 + B + B +...B k 1 )ǫ t θb) = 1 + B +... + B k 1 ), and BθB) = B + B +... + B k ), 1
Time Series Analysis Solutions to problems in Chapter 7 I Solution 7.1 Question 1. As we get by subtraction kx t = 1 + B + B +...B k 1 )ǫ t θb) = 1 + B +... + B k 1 ), and BθB) = B + B +... + B k ), 1
Can a Simple Two-Layer Model Capture the Structure of Easterly Waves?
 Can a Simple Two-Layer Model Capture the Structure of Easterly Waves? Cheryl L. Lacotta 1 Introduction Most tropical storms in the Atlantic, and even many in the eastern Pacific, are due to disturbances
Can a Simple Two-Layer Model Capture the Structure of Easterly Waves? Cheryl L. Lacotta 1 Introduction Most tropical storms in the Atlantic, and even many in the eastern Pacific, are due to disturbances
Coupled Heave-Pitch Motions and Froude Krylov Excitation Forces
 Coupled Heave-Pitch Motions and Froude Krylov Excitation Forces 13.42 Lecture Notes; Spring 2004; c A.H. Techet 1. Coupled Equation of Motion in Heave and Pitch Once we have set up the simple equation
Coupled Heave-Pitch Motions and Froude Krylov Excitation Forces 13.42 Lecture Notes; Spring 2004; c A.H. Techet 1. Coupled Equation of Motion in Heave and Pitch Once we have set up the simple equation
Notes 16 Linearly Independence and Wronskians
 ECE 6382 Fall 2017 David R. Jackson otes 16 Linearly Independence and Wronskians otes are from D. R. Wilton, Dept. of ECE 1 Linear Independence Definition: { φ } A set of functions ( x), n = 1, 2,, is
ECE 6382 Fall 2017 David R. Jackson otes 16 Linearly Independence and Wronskians otes are from D. R. Wilton, Dept. of ECE 1 Linear Independence Definition: { φ } A set of functions ( x), n = 1, 2,, is
Chapter 3 : Linear Differential Eqn. Chapter 3 : Linear Differential Eqn.
 1.0 Introduction Linear differential equations is all about to find the total solution y(t), where : y(t) = homogeneous solution [ y h (t) ] + particular solution y p (t) General form of differential equation
1.0 Introduction Linear differential equations is all about to find the total solution y(t), where : y(t) = homogeneous solution [ y h (t) ] + particular solution y p (t) General form of differential equation
Waves Part 3A: Standing Waves
 Waves Part 3A: Standing Waves Last modified: 24/01/2018 Contents Links Contents Superposition Standing Waves Definition Nodes Anti-Nodes Standing Waves Summary Standing Waves on a String Standing Waves
Waves Part 3A: Standing Waves Last modified: 24/01/2018 Contents Links Contents Superposition Standing Waves Definition Nodes Anti-Nodes Standing Waves Summary Standing Waves on a String Standing Waves
13.1 Ion Acoustic Soliton and Shock Wave
 13 Nonlinear Waves In linear theory, the wave amplitude is assumed to be sufficiently small to ignore contributions of terms of second order and higher (ie, nonlinear terms) in wave amplitude In such a
13 Nonlinear Waves In linear theory, the wave amplitude is assumed to be sufficiently small to ignore contributions of terms of second order and higher (ie, nonlinear terms) in wave amplitude In such a
Notes on Quantum Mechanics
 Notes on Quantum Mechanics Kevin S. Huang Contents 1 The Wave Function 1 1.1 The Schrodinger Equation............................ 1 1. Probability.................................... 1.3 Normalization...................................
Notes on Quantum Mechanics Kevin S. Huang Contents 1 The Wave Function 1 1.1 The Schrodinger Equation............................ 1 1. Probability.................................... 1.3 Normalization...................................
Chapter 16 Waves. Types of waves Mechanical waves. Electromagnetic waves. Matter waves
 Chapter 16 Waves Types of waves Mechanical waves exist only within a material medium. e.g. water waves, sound waves, etc. Electromagnetic waves require no material medium to exist. e.g. light, radio, microwaves,
Chapter 16 Waves Types of waves Mechanical waves exist only within a material medium. e.g. water waves, sound waves, etc. Electromagnetic waves require no material medium to exist. e.g. light, radio, microwaves,
Chapter 5. Shallow Water Equations. 5.1 Derivation of shallow water equations
 Chapter 5 Shallow Water Equations So far we have concentrated on the dynamics of small-scale disturbances in the atmosphere and ocean with relatively simple background flows. In these analyses we have
Chapter 5 Shallow Water Equations So far we have concentrated on the dynamics of small-scale disturbances in the atmosphere and ocean with relatively simple background flows. In these analyses we have
ROSSBY WAVE PROPAGATION
 ROSSBY WAVE PROPAGATION (PHH lecture 4) The presence of a gradient of PV (or q.-g. p.v.) allows slow wave motions generally called Rossby waves These waves arise through the Rossby restoration mechanism,
ROSSBY WAVE PROPAGATION (PHH lecture 4) The presence of a gradient of PV (or q.-g. p.v.) allows slow wave motions generally called Rossby waves These waves arise through the Rossby restoration mechanism,
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension
 Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Reading Quiz 16.05 f = c Slide 16-2 Reading Quiz 16.06 Slide 16-3 Reading Quiz 16.07 Heavier portion looks like a fixed end, pulse is inverted on reflection.
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Reading Quiz 16.05 f = c Slide 16-2 Reading Quiz 16.06 Slide 16-3 Reading Quiz 16.07 Heavier portion looks like a fixed end, pulse is inverted on reflection.
Clicker Question. Is the following equation a solution to the wave equation: y(x,t)=a sin(kx-ωt) (a) yes (b) no
 Is the following equation a solution to the wave equation: y(x,t)=a sin(kx-ωt) (a) yes (b) no Is the following equation a solution to the wave equation: y(x,t)=a sin(kx-ωt) (a) yes (b) no Is the following
Is the following equation a solution to the wave equation: y(x,t)=a sin(kx-ωt) (a) yes (b) no Is the following equation a solution to the wave equation: y(x,t)=a sin(kx-ωt) (a) yes (b) no Is the following
Last name: name: 1. (B A A B)dx = (A B) = (A B) nds. which implies that B Adx = A Bdx + (A B) nds.
 Last name: name: Notes, books, and calculators are not authorized. Show all your work in the blank space you are given on the exam sheet. Answers with no justification will not be graded. Question : Let
Last name: name: Notes, books, and calculators are not authorized. Show all your work in the blank space you are given on the exam sheet. Answers with no justification will not be graded. Question : Let
Effective Depth of Ekman Layer.
 5.5: Ekman Pumping Effective Depth of Ekman Layer. 2 Effective Depth of Ekman Layer. Defining γ = f/2k, we derived the solution u = u g (1 e γz cos γz) v = u g e γz sin γz corresponding to the Ekman spiral.
5.5: Ekman Pumping Effective Depth of Ekman Layer. 2 Effective Depth of Ekman Layer. Defining γ = f/2k, we derived the solution u = u g (1 e γz cos γz) v = u g e γz sin γz corresponding to the Ekman spiral.
Dispersion relations, stability and linearization
 Dispersion relations, stability and linearization 1 Dispersion relations Suppose that u(x, t) is a function with domain { < x 0}, and it satisfies a linear, constant coefficient partial differential
Dispersion relations, stability and linearization 1 Dispersion relations Suppose that u(x, t) is a function with domain { < x 0}, and it satisfies a linear, constant coefficient partial differential
LOWELL. MICHIGAN, THURSDAY, MAY 23, Schools Close. method of distribution. t o t h e b o y s of '98 a n d '18. C o m e out a n d see t h e m get
 UY Y 99 U XXX 5 Q == 5 K 8 9 $8 7 Y Y 8 q 6 Y x) 5 7 5 q U «U YU x q Y U ) U Z 9 Y 7 x 7 U x U x 9 5 & U Y U U 7 8 9 x 5 x U x x ; x x [ U K»5 98 8 x q 8 q K x Y Y x K Y 5 ~ 8» Y x ; ; ; ; ; ; 8; x 7;
UY Y 99 U XXX 5 Q == 5 K 8 9 $8 7 Y Y 8 q 6 Y x) 5 7 5 q U «U YU x q Y U ) U Z 9 Y 7 x 7 U x U x 9 5 & U Y U U 7 8 9 x 5 x U x x ; x x [ U K»5 98 8 x q 8 q K x Y Y x K Y 5 ~ 8» Y x ; ; ; ; ; ; 8; x 7;
1 Basics of Quantum Mechanics
 1 Basics of Quantum Mechanics 1.1 Admin The course is based on the book Quantum Mechanics (2nd edition or new international edition NOT 1st edition) by Griffiths as its just genius for this level. There
1 Basics of Quantum Mechanics 1.1 Admin The course is based on the book Quantum Mechanics (2nd edition or new international edition NOT 1st edition) by Griffiths as its just genius for this level. There
Physics 9 Summer 2011 Homework 4 - Solutions Friday June 24, 2011
 Physics 9 Summer 011 Homework 4 - s Friday June 4, 011 Make sure your name is on your homework, and please box your final answer. Because we will be giving partial credit, be sure to attempt all the problems,
Physics 9 Summer 011 Homework 4 - s Friday June 4, 011 Make sure your name is on your homework, and please box your final answer. Because we will be giving partial credit, be sure to attempt all the problems,
Today in Physics 218: back to electromagnetic waves
 Today in Physics 18: back to electromagnetic waves Impedance Plane electromagnetic waves Energy and momentum in plane electromagnetic waves Radiation pressure Artist s conception of a solar sail: a spacecraft
Today in Physics 18: back to electromagnetic waves Impedance Plane electromagnetic waves Energy and momentum in plane electromagnetic waves Radiation pressure Artist s conception of a solar sail: a spacecraft
Course Updates. 2) This week: Electromagnetic Waves +
 Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr1/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Assignment #11 due Wednesday 2) This week: Electromagnetic Waves + 3) In the home stretch [review schedule]
Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr1/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Assignment #11 due Wednesday 2) This week: Electromagnetic Waves + 3) In the home stretch [review schedule]
(TRAVELLING) 1D WAVES. 1. Transversal & Longitudinal Waves
 (TRAVELLING) 1D WAVES 1. Transversal & Longitudinal Waves Objectives After studying this chapter you should be able to: Derive 1D wave equation for transversal and longitudinal Relate propagation speed
(TRAVELLING) 1D WAVES 1. Transversal & Longitudinal Waves Objectives After studying this chapter you should be able to: Derive 1D wave equation for transversal and longitudinal Relate propagation speed
Symmetric Instability and Rossby Waves
 Chapter 8 Symmetric Instability and Rossby Waves We are now in a position to begin investigating more complex disturbances in a rotating, stratified environment. Most of the disturbances of interest are
Chapter 8 Symmetric Instability and Rossby Waves We are now in a position to begin investigating more complex disturbances in a rotating, stratified environment. Most of the disturbances of interest are
Linear Advection Equation
 Linear Advection Equation Numerical Methods Laboratory Modelling the Climate System ARC Centre of Excellence for Climate System Science 2nd Annual Winter School 18 June 2013 1 Analytical Solution The linear
Linear Advection Equation Numerical Methods Laboratory Modelling the Climate System ARC Centre of Excellence for Climate System Science 2nd Annual Winter School 18 June 2013 1 Analytical Solution The linear
2 The incompressible Kelvin-Helmholtz instability
 Hydrodynamic Instabilities References Chandrasekhar: Hydrodynamic and Hydromagnetic Instabilities Landau & Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics Shu: Gas Dynamics 1 Introduction Instabilities are an important aspect
Hydrodynamic Instabilities References Chandrasekhar: Hydrodynamic and Hydromagnetic Instabilities Landau & Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics Shu: Gas Dynamics 1 Introduction Instabilities are an important aspect
Salmon: Introduction to ocean waves
 3 Many waves In the previous lecture, we considered the case of two basic waves propagating in one horizontal dimension. However, Proposition #2 lets us have as many basic waves as we want. Suppose we
3 Many waves In the previous lecture, we considered the case of two basic waves propagating in one horizontal dimension. However, Proposition #2 lets us have as many basic waves as we want. Suppose we
TITLE: The Steady Linear Response of a Spherical Atmosphere to Thermal and Orographic Forcing AUTHOR: Brian J. Hoskins David J.
 TITLE: AUTHOR: The Steay Linear Response of a Spherical Atmosphere to Thermal an Orographic Forcing Brian J. Hoskins Davi J. Karoly YEAR: 1981 REVIEWED: January 25, 2011 Reasons for Review: What are the
TITLE: AUTHOR: The Steay Linear Response of a Spherical Atmosphere to Thermal an Orographic Forcing Brian J. Hoskins Davi J. Karoly YEAR: 1981 REVIEWED: January 25, 2011 Reasons for Review: What are the
MATH FALL 2014 HOMEWORK 10 SOLUTIONS
 Problem 1. MATH 241-2 FA 214 HOMEWORK 1 SOUTIONS Note that u E (x) 1 ( x) is an equilibrium distribution for the homogeneous pde that satisfies the given boundary conditions. We therefore want to find
Problem 1. MATH 241-2 FA 214 HOMEWORK 1 SOUTIONS Note that u E (x) 1 ( x) is an equilibrium distribution for the homogeneous pde that satisfies the given boundary conditions. We therefore want to find
A simple model of topographic Rossby waves in the ocean
 A simple model of topographic Rossby waves in the ocean V.Teeluck, S.D.Griffiths, C.A.Jones University of Leeds April 18, 2013 V.Teeluck (University of Leeds) Topographic Rossby waves (TRW) in the ocean
A simple model of topographic Rossby waves in the ocean V.Teeluck, S.D.Griffiths, C.A.Jones University of Leeds April 18, 2013 V.Teeluck (University of Leeds) Topographic Rossby waves (TRW) in the ocean
Complex Number Review:
 Complex Numbers and Waves Review 1 of 14 Complex Number Review: Wave functions Ψ are in general complex functions. So it's worth a quick review of complex numbers, since we'll be dealing with this all
Complex Numbers and Waves Review 1 of 14 Complex Number Review: Wave functions Ψ are in general complex functions. So it's worth a quick review of complex numbers, since we'll be dealing with this all
SAMPLE CHAPTERS UNESCO EOLSS WAVES IN THE OCEANS. Wolfgang Fennel Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde (IOW) an der Universität Rostock,Germany
 WAVES IN THE OCEANS Wolfgang Fennel Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde (IOW) an der Universität Rostock,Germany Keywords: Wind waves, dispersion, internal waves, inertial oscillations, inertial waves,
WAVES IN THE OCEANS Wolfgang Fennel Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde (IOW) an der Universität Rostock,Germany Keywords: Wind waves, dispersion, internal waves, inertial oscillations, inertial waves,
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar
 Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
Chapter 2. The continuous equations
 Chapter. The continuous equations Fig. 1.: Schematic of a forecast with slowly varying weather-related variations and superimposed high frequency Lamb waves. Note that even though the forecast of the slow
Chapter. The continuous equations Fig. 1.: Schematic of a forecast with slowly varying weather-related variations and superimposed high frequency Lamb waves. Note that even though the forecast of the slow
MA4001 Engineering Mathematics 1 Lecture 15 Mean Value Theorem Increasing and Decreasing Functions Higher Order Derivatives Implicit Differentiation
 MA4001 Engineering Mathematics 1 Lecture 15 Mean Value Theorem Increasing and Decreasing Functions Higher Order Derivatives Implicit Differentiation Dr. Sarah Mitchell Autumn 2014 Rolle s Theorem Theorem
MA4001 Engineering Mathematics 1 Lecture 15 Mean Value Theorem Increasing and Decreasing Functions Higher Order Derivatives Implicit Differentiation Dr. Sarah Mitchell Autumn 2014 Rolle s Theorem Theorem
Class 30: Outline. Hour 1: Traveling & Standing Waves. Hour 2: Electromagnetic (EM) Waves P30-
 Class 30: Outline Hour 1: Traveling & Standing Waves Hour : Electromagnetic (EM) Waves P30-1 Last Time: Traveling Waves P30- Amplitude (y 0 ) Traveling Sine Wave Now consider f(x) = y = y 0 sin(kx): π
Class 30: Outline Hour 1: Traveling & Standing Waves Hour : Electromagnetic (EM) Waves P30-1 Last Time: Traveling Waves P30- Amplitude (y 0 ) Traveling Sine Wave Now consider f(x) = y = y 0 sin(kx): π
1D Wave PDE. Introduction to Partial Differential Equations part of EM, Scalar and Vector Fields module (PHY2064) Richard Sear.
 Introduction to Partial Differential Equations part of EM, Scalar and Vector Fields module (PHY2064) November 12, 2018 Wave equation in one dimension This lecture Wave PDE in 1D Method of Separation of
Introduction to Partial Differential Equations part of EM, Scalar and Vector Fields module (PHY2064) November 12, 2018 Wave equation in one dimension This lecture Wave PDE in 1D Method of Separation of
Floquet Theory for Internal Gravity Waves in a Density-Stratified Fluid. Yuanxun Bill Bao Senior Supervisor: Professor David J. Muraki August 3, 2012
 Floquet Theory for Internal Gravity Waves in a Density-Stratified Fluid Yuanxun Bill Bao Senior Supervisor: Professor David J. Muraki August 3, 212 Density-Stratified Fluid Dynamics Density-Stratified
Floquet Theory for Internal Gravity Waves in a Density-Stratified Fluid Yuanxun Bill Bao Senior Supervisor: Professor David J. Muraki August 3, 212 Density-Stratified Fluid Dynamics Density-Stratified
t tendency advection convergence twisting baroclinicity
 RELATIVE VORTICITY EQUATION Newton s law in a rotating frame in z-coordinate (frictionless): U + U U = 2Ω U Φ α p U + U U 2 + ( U) U = 2Ω U Φ α p Applying to both sides, and noting ω U and using identities
RELATIVE VORTICITY EQUATION Newton s law in a rotating frame in z-coordinate (frictionless): U + U U = 2Ω U Φ α p U + U U 2 + ( U) U = 2Ω U Φ α p Applying to both sides, and noting ω U and using identities
Recurrences in Quantum Walks
 Recurrences in Quantum Walks M. Štefaňák (1), I. Jex (1), T. Kiss (2) (1) Department of Physics, FJFI ČVUT in Prague, Czech Republic (2) Department of Nonlinear and Quantum Optics, RISSPO, Hungarian Academy
Recurrences in Quantum Walks M. Štefaňák (1), I. Jex (1), T. Kiss (2) (1) Department of Physics, FJFI ČVUT in Prague, Czech Republic (2) Department of Nonlinear and Quantum Optics, RISSPO, Hungarian Academy
Understanding the local and global impacts of model physics changes
 ECMWF Annual Seminar 2008 MJR 1 Understanding the local and global impacts of model physics changes Mark Rodwell Work with Thomas Jung 4 September 2008 Thanks to: MJR 2 Motivation The real world and GCMs
ECMWF Annual Seminar 2008 MJR 1 Understanding the local and global impacts of model physics changes Mark Rodwell Work with Thomas Jung 4 September 2008 Thanks to: MJR 2 Motivation The real world and GCMs
The Euler Equation of Gas-Dynamics
 The Euler Equation of Gas-Dynamics A. Mignone October 24, 217 In this lecture we study some properties of the Euler equations of gasdynamics, + (u) = ( ) u + u u + p = a p + u p + γp u = where, p and u
The Euler Equation of Gas-Dynamics A. Mignone October 24, 217 In this lecture we study some properties of the Euler equations of gasdynamics, + (u) = ( ) u + u u + p = a p + u p + γp u = where, p and u
BASIC WAVE CONCEPTS. Reading: Main 9.0, 9.1, 9.3 GEM 9.1.1, Giancoli?
 1 BASIC WAVE CONCEPTS Reading: Main 9.0, 9.1, 9.3 GEM 9.1.1, 9.1.2 Giancoli? REVIEW SINGLE OSCILLATOR: The oscillation functions you re used to describe how one quantity (position, charge, electric field,
1 BASIC WAVE CONCEPTS Reading: Main 9.0, 9.1, 9.3 GEM 9.1.1, 9.1.2 Giancoli? REVIEW SINGLE OSCILLATOR: The oscillation functions you re used to describe how one quantity (position, charge, electric field,
Recurrences and Full-revivals in Quantum Walks
 Recurrences and Full-revivals in Quantum Walks M. Štefaňák (1), I. Jex (1), T. Kiss (2) (1) Department of Physics, Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague,
Recurrences and Full-revivals in Quantum Walks M. Štefaňák (1), I. Jex (1), T. Kiss (2) (1) Department of Physics, Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague,
u g z = g T y (1) f T Margules Equation for Frontal Slope
 Margules Equation for Frontal Slope u g z = g f T T y (1) Equation (1) is the thermal wind relation for the west wind geostrophic component of the flow. For the purposes of this derivation, we assume that
Margules Equation for Frontal Slope u g z = g f T T y (1) Equation (1) is the thermal wind relation for the west wind geostrophic component of the flow. For the purposes of this derivation, we assume that
Class 15 : Electromagnetic Waves
 Class 15 : Electromagnetic Waves Wave equations Why do electromagnetic waves arise? What are their properties? How do they transport energy from place to place? Recap (1) In a region of space containing
Class 15 : Electromagnetic Waves Wave equations Why do electromagnetic waves arise? What are their properties? How do they transport energy from place to place? Recap (1) In a region of space containing
WAVES CP4 REVISION LECTURE ON. The wave equation. Traveling waves. Standing waves. Dispersion. Phase and group velocities.
 CP4 REVISION LECTURE ON WAVES The wave equation. Traveling waves. Standing waves. Dispersion. Phase and group velocities. Boundary effects. Reflection and transmission of waves. !"#$%&''(%)*%+,-.%/%+,01%
CP4 REVISION LECTURE ON WAVES The wave equation. Traveling waves. Standing waves. Dispersion. Phase and group velocities. Boundary effects. Reflection and transmission of waves. !"#$%&''(%)*%+,-.%/%+,01%
7. introduction to 3D scattering 8. ISAR. 9. antenna theory (a) antenna examples (b) vector and scalar potentials (c) radiation in the far field
 .. Outline 7. introduction to 3D scattering 8. ISAR 9. antenna theory (a) antenna examples (b) vector and scalar potentials (c) radiation in the far field 10. spotlight SAR 11. stripmap SAR Dipole antenna
.. Outline 7. introduction to 3D scattering 8. ISAR 9. antenna theory (a) antenna examples (b) vector and scalar potentials (c) radiation in the far field 10. spotlight SAR 11. stripmap SAR Dipole antenna
Applied Nuclear Physics Homework #2
 22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics Homework #2 Author: Lulu Li Professor: Bilge Yildiz, Paola Cappellaro, Ju Li, Sidney Yip Oct. 7, 2011 2 1. Answers: Refer to p16-17 on Krane, or 2.35 in Griffith. (a) x
22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics Homework #2 Author: Lulu Li Professor: Bilge Yildiz, Paola Cappellaro, Ju Li, Sidney Yip Oct. 7, 2011 2 1. Answers: Refer to p16-17 on Krane, or 2.35 in Griffith. (a) x
Physics 142 Mechanical Waves Page 1. Mechanical Waves
 Physics 142 Mechanical Waves Page 1 Mechanical Waves This set of notes contains a review of wave motion in mechanics, emphasizing the mathematical formulation that will be used in our discussion of electromagnetic
Physics 142 Mechanical Waves Page 1 Mechanical Waves This set of notes contains a review of wave motion in mechanics, emphasizing the mathematical formulation that will be used in our discussion of electromagnetic
iii. We introduce and discuss the most important classical example of wave phenomena, electromagnetic waves and light.
 Chapter 8 Traveling Waves In this chapter, we show how the same physics that leads to standing wave oscillations also gives rise to waves that move in space as well as time We then go on to introduce the
Chapter 8 Traveling Waves In this chapter, we show how the same physics that leads to standing wave oscillations also gives rise to waves that move in space as well as time We then go on to introduce the
Chapter 33. Alternating Current Circuits
 Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits 1 Capacitor Resistor + Q = C V = I R R I + + Inductance d I Vab = L dt AC power source The AC power source provides an alternative voltage, Notation - Lower case
Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits 1 Capacitor Resistor + Q = C V = I R R I + + Inductance d I Vab = L dt AC power source The AC power source provides an alternative voltage, Notation - Lower case
Physics Dec Time Independent Solutions of the Diffusion Equation
 Physics 301 10-Dec-2004 33-1 Time Independent Solutions of the Diffusion Equation In some cases we ll be interested in the time independent solution of the diffusion equation Why would be interested in
Physics 301 10-Dec-2004 33-1 Time Independent Solutions of the Diffusion Equation In some cases we ll be interested in the time independent solution of the diffusion equation Why would be interested in
